Successful cataract surgery involves a multifactorial process that relies on numerous interconnected assessment, planning, and execution procedures. Phacodynamics, which is the effects of the equipment used to perform a cataract procedure on the internal environment of the eye, must be thoroughly understood to maintain a stable anterior chamber and to minimize damage due to the heat produced by ultrasonic energy during phacoemulsification. New technologies, such as optical coherence tomography and femtosecond (FS) laser, can be applied to several diagnostic and procedural components of the surgery.
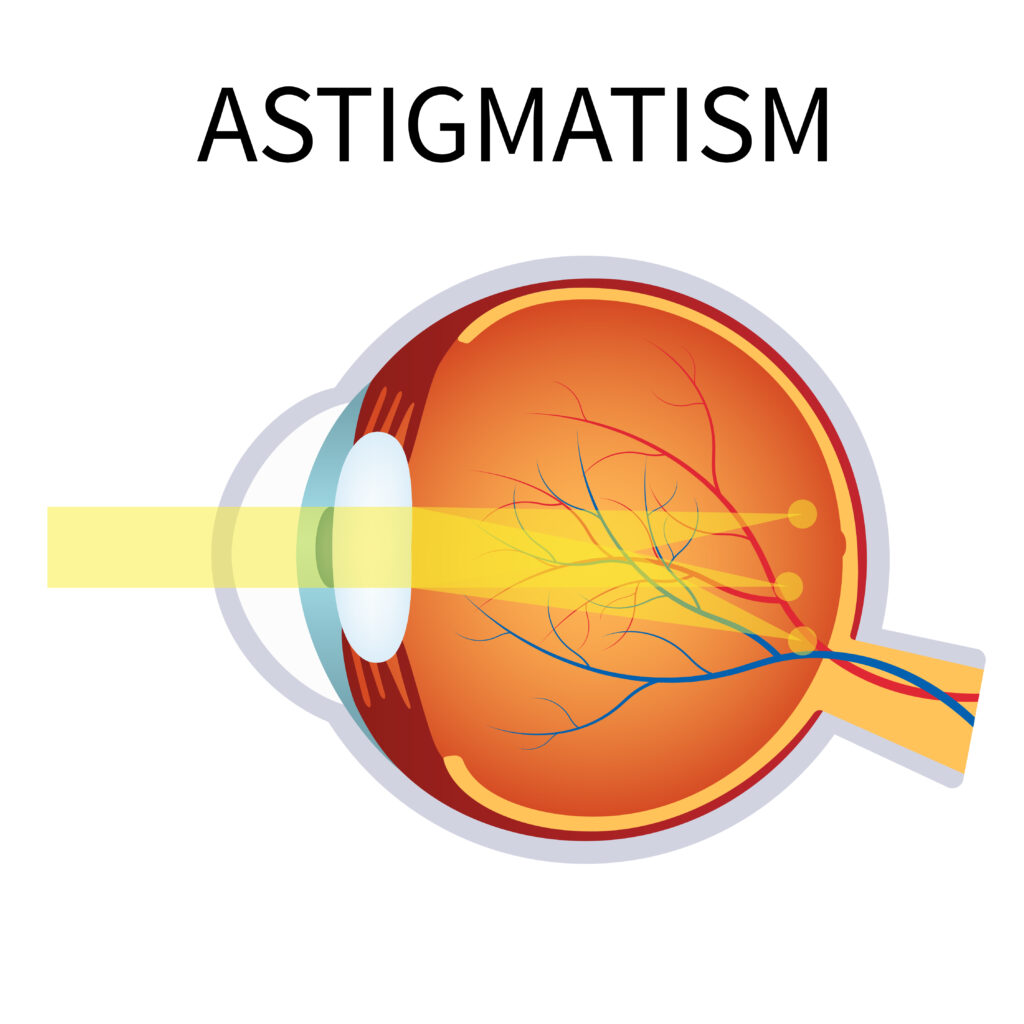
Astigmatism can now be corrected during cataract surgery, using peripheral corneal relaxing incisions or toric intraocular lens implantation. The surgeon can select from a growing range of intraocular lenses to achieve the refractive outcomes desired by the patient. In refractive surgery, FS laser is also used to correct astigmatism, and it can be employed for high-precision cutting of LASIK flaps.

 Original article from Healio
Original article from Healio